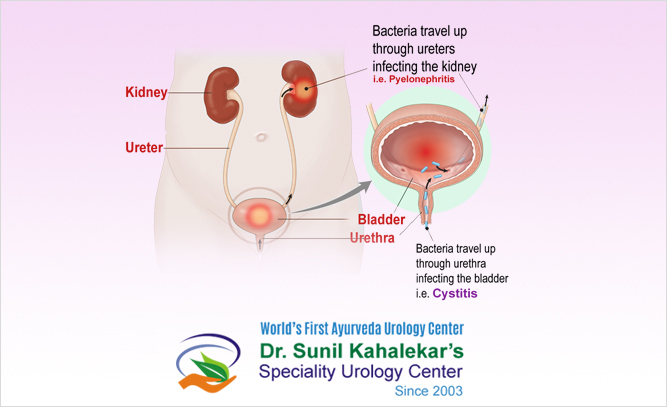
RECURRENT URINARY INFECTION
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are among the most common bacterial infections in women, accounting for about 25 percent of all infections. Approximately 50 to 60 percent of women will have at least one urinary tract infection during their lifetime. The main cause of recurrent urinary tract infections (RUTIs) is reinfection by the same bacteria.
Recurrent UTIs (RUTI) are mainly caused by reinfection by the same pathogen. Having frequent sexual intercourse is one of the greatest risk factors for RUTIs.
Women are more prone to urinary tract infections than men because the female urethra is shorter than the male urethra. A shorter urethra makes it easier for bacteria to reach the bladder. One of the major risk factors for RUTIs is frequent sexual intercourse.
Untreated urinary tract infections may spread to the kidney, causing more pain and illness. It can also cause sepsis. The term urosepsis is usually used to describe sepsis caused by a UTI. Sometimes incorrectly called blood poisoning, sepsis is the body’s often deadly response to infection or injury.
To Prevent Recurrent UTIs
- Stay well-hydrated.
- Urinate regularly.
- Wipe from front to back.
- Go to the bathroom after having sex.
- Take showers rather than baths.
- Avoid using douches and other products.
- Wear cotton panties.
- Consider preventive antibiotics.